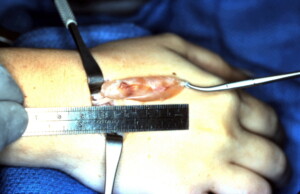
Ganglion Doral Wrist EDC large
Ganglions form in areas where synovium is present i.e.. joints or tendon sheaths. Synovium is a material that secretes synovial fluid to lubricate surfaces and prevent friction. In a joint it allows cartilage covering the ends of bones to glide over one another and for tendons it allows migration of the tendon within the tendon sheath and prevents friction with adjacent tendons.
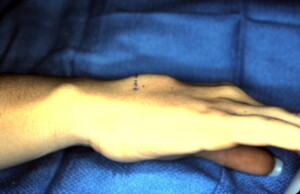 Lateral view of a large dorsal wrist ganglion originating from the EDC (Extensor Digitorum Comminus) tendon synovium with a transverse incision marked out over the mass for excision.
Lateral view of a large dorsal wrist ganglion originating from the EDC (Extensor Digitorum Comminus) tendon synovium with a transverse incision marked out over the mass for excision.
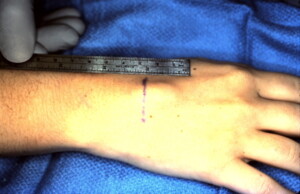 Dorsal View of the same dorsal wrist mass.
Dorsal View of the same dorsal wrist mass.
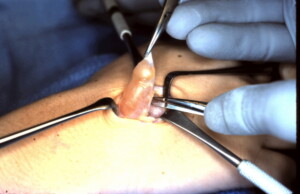 Ganglion being excised. Ganglions are typically filled with thick gelatinous material and frequently are septated and is why they are difficult to completely aspirate.
Ganglion being excised. Ganglions are typically filled with thick gelatinous material and frequently are septated and is why they are difficult to completely aspirate.