Retained Foreign Body Gun Shot Wound Pellets
Assessment of a patient with a puncture wound and suspected foreign body begins with a careful history and physical examination. Patients who present with a wound or localized pain following penetrating trauma should be questioned regarding the specific timing and nature of the injury, the level of wound contamination and any materials involved in the injury. Foreign bodies are most commonly composed of wood, glass, or metal. A careful assessment of the patient’s current symptoms should be sought, including the location, quality, severity and radiation of pain, the presence of a foreign body sensation, signs of infection including; swelling, warmth, or redness to the wound and any neurologic symptoms (including motor or sensory deficits).
If exploration and surgical removal of a foreign body of a puncture wound is necessary, it should be performed under sterile conditions, adequate anesthesia and tourniquet control. Infection is very commonly associated with puncture woulds and retained foreign bodies. Appropriate antibiotic treatment is recommended.
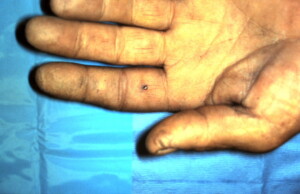
Single puncture wound evident over volar surface of the proximal phalanx of the index finger.
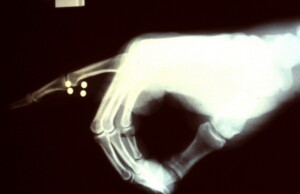
X-ray revealing 4 pellets entered the index finger with a short burst from this automatic weapon.
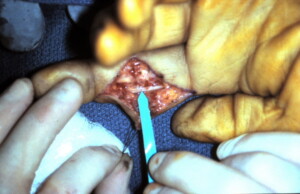
Exploration of the finger for removal and debridement of wound reveals an intact radial digital nerve despite some preoperative sensory deficit likely resulting from a contusion from the blast.
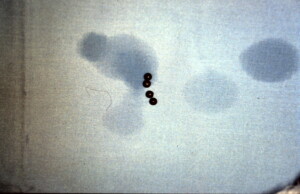
Foreign bodies (Pellets) removed.