Palmaris Brevis Muscle Hypertrophy
The palmaris brevis is usually a small, quadrilateral muscle within the palm of the hand. It is situated superficial to the hypothenar eminence. It is generally a very thin muscle with very little function. In some patients it can be hypertrophied and quite prominent. It originates from the flexor retinaculum and the palmar aponeurosis and inserts into the dermis of the ulnar side of the palmar skin. When it contracts it deepens the hollow of the palm and wrinkles the skin on the ulnar side of the palm. These two actions in combination steady the skin on the palmar side of the hand while griping. This muscle needs to be divided in a standard open carpal tunnel release procedure, which is one reason why an endoscopic carpal tunnel release is less painful and is associated with a faster recovery than an open carpal tunnel release, since this muscle does not need to be divided in an endoscopic procedure. Dr. Woloszyn at the hand treatment center has more than 20 years experience performing the minimally invasive endoscopic carpal tunnel release procedure.
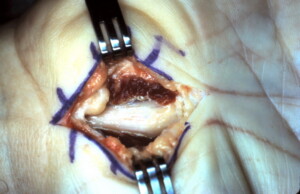 Intra-operative view of a the hypertrophic palmaris brevis muscle that need to be divided in an open carpal tunnel release procedure. This muscle can be spared in an endoscopic carpal tunnel release procedure and therefore be associated with less pain and earlier recovery.
Intra-operative view of a the hypertrophic palmaris brevis muscle that need to be divided in an open carpal tunnel release procedure. This muscle can be spared in an endoscopic carpal tunnel release procedure and therefore be associated with less pain and earlier recovery.



